Fractional investing is revolutionizing how people invest. Instead of needing a large sum to buy a whole stock, you can now buy tiny pieces, or “fractions,” of many different investments. This opens up a world of opportunities for everyone, from beginners just starting out to seasoned investors looking to diversify their portfolios.
This approach is transforming the investment landscape by lowering barriers to entry and allowing broader access to a wider range of assets. Imagine having the power to invest in stocks, bonds, and even real estate, all with a fraction of the usual investment minimum. This flexibility is key to building a diversified portfolio tailored to your unique financial goals.
Introduction to Fractional Investing
Fractional investing is a relatively new way to participate in the stock market, and it’s quickly gaining popularity. It allows individuals to invest in stocks and other securities without needing to buy a whole share. This approach democratizes access to the market, making it easier for people with smaller amounts of capital to invest in a diverse range of assets.This method differs significantly from traditional investing, where you’d typically buy a whole share of a particular stock.
Fractional investing breaks down those shares into smaller, more manageable pieces, providing greater flexibility and broader portfolio diversification. It’s a powerful tool for beginners and seasoned investors alike, offering opportunities previously limited to those with substantial capital.
Fractional investing is a great way to get into the market with smaller amounts. It allows you to diversify your portfolio, which is key to long-term success. This approach can be especially helpful for accessing assets that might otherwise be too expensive for individual investors. And, when using fractional investing, you can potentially gain exposure to more complex assets like cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, like those available on some platforms.
Stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to a fiat currency, which can be helpful in managing risk within a fractional investing strategy. It’s a smart way to manage your investment portfolio.
Key Characteristics of Fractional Investing
Fractional investing is distinguished by its accessibility and flexibility. Unlike traditional stock purchases, fractional investing enables investors to buy portions of a stock share. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios more effectively by allocating funds across multiple companies, sectors, and asset classes. This feature significantly reduces the capital barrier to entry, enabling participation for a wider range of investors.
Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of fractional investing has evolved over time. Initially, fractional ownership was primarily seen in real estate, like fractional ownership of vacation homes. Later, it was adapted to the stock market, driven by the rise of online brokerage platforms. These platforms made it easier for individuals to access and manage fractional shares, ultimately lowering the investment threshold and broadening the market.
The evolution of fractional investing is a testament to the ongoing development of financial technology, aimed at democratizing access to investment opportunities.
Comparison with Traditional Stock Purchases
| Method | Cost | Access | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fractional Investing | Investors can buy fractions of shares, reducing the initial investment required. | Easier access to a wider range of assets and diversification opportunities, opening up investment possibilities to a broader audience. | The risk is similar to traditional investing, as the value of the underlying assets can fluctuate. |
| Traditional Stock Purchases | Requires purchasing a whole share of a particular stock, often with a higher minimum investment. | Limited to those with sufficient capital to buy whole shares, potentially limiting investment diversification. | Similar to fractional investing, the risk depends on the performance of the underlying asset. |
This table highlights the key differences between fractional investing and traditional stock purchases, focusing on cost, access, and risk factors. The table clearly shows how fractional investing significantly lowers the investment barrier, broadening the scope of participation.
Benefits of Fractional Investing
Fractional investing is rapidly gaining popularity as a way for individual investors to access a wider range of investment opportunities. It streamlines the process of building a diversified portfolio and can be a powerful tool for achieving financial goals. This approach empowers individuals with limited capital to participate in the market, effectively lowering the barriers to entry.This approach democratizes access to investments previously exclusive to those with substantial funds.
It allows investors to tap into a broader spectrum of asset classes and manage risk more effectively, ultimately helping them reach their financial objectives.
Advantages for Individual Investors
Fractional investing offers significant advantages for individual investors. It allows them to diversify their portfolios without needing large sums of money for each investment. This approach is particularly beneficial for those starting their investment journey or those seeking to augment their existing portfolios with diverse asset classes.
Broadening Investment Portfolios
Fractional investing expands the horizons of investment options available to individual investors. It opens doors to assets previously inaccessible due to minimum investment requirements. This increased accessibility translates to a broader range of opportunities to diversify and optimize portfolios, potentially leading to higher returns and a more balanced risk profile.
Diversification Benefits
Diversification is a cornerstone of sound investment strategy. Fractional investing empowers investors to spread their investments across a variety of asset classes, from stocks and bonds to real estate and even alternative assets. This reduces overall portfolio risk, as performance fluctuations in one area are offset by potential gains in others. A well-diversified portfolio is better equipped to weather market downturns and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Lowering the Barrier to Entry
A significant benefit of fractional investing is the substantial reduction in the minimum investment amount. This dramatically lowers the barrier to entry for new investors, allowing them to start investing with smaller capital. This accessibility fosters greater participation in the market and encourages financial planning, regardless of the initial investment sum.
Examples of Accessible Assets
Fractional investing allows access to a variety of investment assets. Common examples include:
- Stocks of publicly traded companies, allowing investors to own a portion of a company’s shares.
- Real estate investment trusts (REITs), offering exposure to the real estate market without needing a large upfront investment.
- Private equity funds, enabling participation in investments typically reserved for high-net-worth individuals.
- Precious metals, providing a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
- Peer-to-peer lending platforms, allowing investors to lend money to individuals or businesses directly.
Reduced Investment Minimums
The following table illustrates the reduced investment minimums compared to traditional investment approaches.
| Asset Type | Fractional Minimum | Traditional Minimum | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | $50-$100 | $500-$1000+ | $450-$900+ |
| REITs | $50-$100 | $1000+ | $950+ |
| Bonds | $50-$100 | $1000+ | $950+ |
| Alternative Assets (e.g., Private Equity) | $500-$1000 | $25,000+ | $24,500+ |
Note: Fractional minimums and traditional minimums can vary depending on the specific platform and investment. Savings figures are estimates illustrating the potential savings by using fractional investing.
Fractional investing is a cool way to get involved in the stock market, even with a small amount of money. It’s like a smaller version of traditional investing, and it often allows access to investments you might not be able to afford otherwise. This approach is increasingly popular with new investors, and it’s frequently paired with the rise of challenger banks, which are often more accessible and offer better rates and services.
Challenger banks, like these , are shaking up the traditional financial industry and offering fresh ways to manage money, making fractional investing even more appealing to those looking for a new way to grow their portfolios.
Platforms and Tools for Fractional Investing
Fractional investing platforms have revolutionized access to the investment world. These platforms allow individuals to invest in assets previously out of reach due to high minimum investment requirements. This democratization of investment opens up opportunities for broader participation and portfolio diversification.Many fractional investing platforms offer a user-friendly interface and tools that make navigating the complexities of the market easier.
This accessibility is a key benefit, particularly for novice investors.
Popular Fractional Investing Platforms
Several platforms have emerged as leaders in the fractional investing space. These platforms typically cater to different investor needs and preferences. Understanding the various options available is crucial for selecting a platform that aligns with your individual investment goals.
- Robinhood: A popular choice known for its user-friendly interface and extensive selection of stocks and ETFs. Robinhood is known for its zero-commission trading, which can significantly reduce transaction costs.
- Fidelity: A well-established brokerage firm that offers a comprehensive suite of investment products, including fractional shares. Fidelity often provides robust research tools and educational resources to support investors.
- Webull: Another user-friendly platform with a strong focus on low-cost trading and a wide selection of stocks and ETFs. Webull frequently features promotions and incentives for new users.
- SoFi: A financial technology company that offers fractional investing alongside other financial services, including loans and banking products. SoFi’s platform is often integrated with its broader financial services ecosystem.
Comparing Platform Features
A comparison of key features can help you choose the right platform. Factors like minimum investment amounts, fees, and available asset types play a crucial role in selecting a platform that meets your needs.
| Platform | Account Minimum | Fees | Asset Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robinhood | $0 | Typically zero commission, but potential for other fees (e.g., inactivity fees) | Stocks, ETFs |
| Fidelity | Variable, often low | Variable, depending on the specific investment product | Stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, bonds |
| Webull | $0 | Typically zero commission, but potential for other fees (e.g., inactivity fees) | Stocks, ETFs |
| SoFi | Variable, often low | Variable, depending on the specific investment product | Stocks, ETFs, and other financial products |
Technology’s Role in Accessibility
Technology has been instrumental in making fractional investing accessible to a wider range of investors. Mobile-first platforms and intuitive interfaces have simplified the process for individuals who may not have prior experience with traditional investing. Furthermore, the use of algorithms and advanced data analysis tools can help investors make more informed decisions.
Setting Up a Fractional Investing Account
The process of opening a fractional investing account typically involves a few straightforward steps. First, you will need to create an account on the chosen platform. Next, you will need to fund your account. Finally, you can begin selecting and investing in fractional shares of various assets. The steps are often straightforward and guided by the platform’s user interface.
Security Measures
Fractional investing platforms utilize robust security measures to protect investor funds. These measures often include multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits. The specific protocols used may vary among platforms, but the goal remains consistent: ensuring the security of investor assets.
Risks and Considerations of Fractional Investing
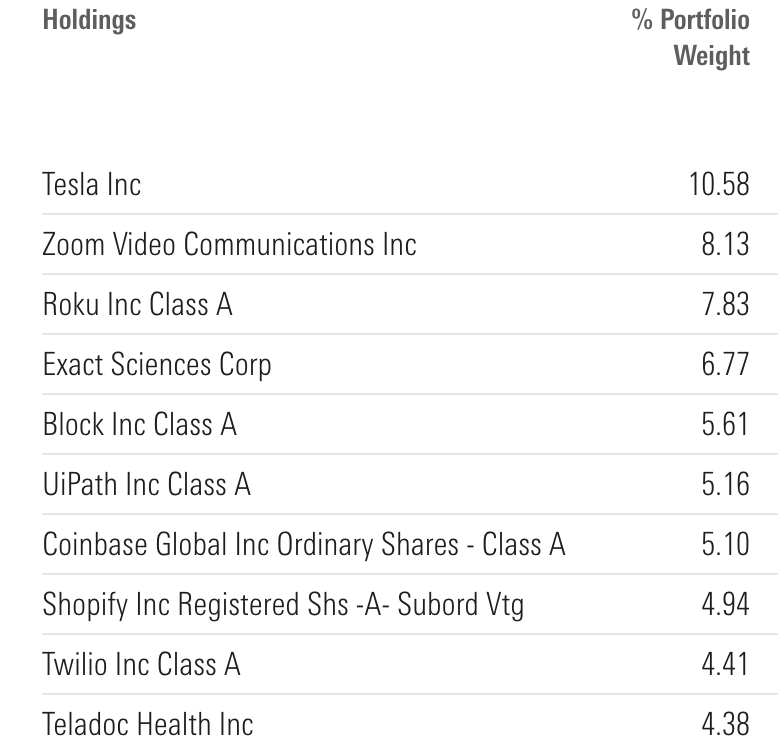
Source: storyblok.com
Fractional investing, while offering access to a wider range of investments, comes with inherent risks that need careful consideration. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate strategies to mitigate them is crucial for successful participation. Investors should be aware of the potential downsides and the factors that could negatively impact their returns before making any investment decisions.Fractional investing, like traditional investing, carries the potential for losses.
Investors should not view fractional investing as a guaranteed path to riches but rather as a way to potentially diversify their portfolios and participate in larger markets.
Potential Risks Associated with Fractional Investing
Fractional investing, despite its benefits, presents certain risks that are worth noting. One key risk lies in the potential for illiquidity, meaning that it might be challenging to quickly sell fractional shares. This can be particularly true for smaller or less-traded companies or sectors. Additionally, the complexity of some fractional investment platforms can make it challenging for less-experienced investors to fully understand the nuances of the investment strategies and associated risks.
Finally, the sheer volume of choices available can lead to a phenomenon known as analysis paralysis, where investors struggle to make informed decisions amidst the plethora of opportunities.
Factors Impacting Investment Returns
Numerous factors can influence the returns of fractional investments. Market conditions, both local and global, play a critical role. Economic downturns, recessions, or geopolitical instability can significantly impact investment performance. Company-specific factors such as management quality, financial health, and industry trends are crucial determinants of success. The broader market environment, including interest rate changes, inflation, and regulatory changes, can all affect investment returns.
These market forces, coupled with company-specific conditions, combine to determine investment success or failure.
Comparison of Risks with Traditional Investing, Fractional investing
While fractional investing shares some similarities with traditional investing in terms of potential risk, key differences exist. Traditional investing often involves direct ownership of assets, offering greater control and transparency. Fractional investing, on the other hand, relies on platforms that act as intermediaries, which can introduce an element of complexity and potential operational risk. The degree of diversification is also a key consideration; fractional investing facilitates broader diversification but can also expose investors to a greater number of individual risks across multiple companies and industries.
Managing Risk within a Fractional Investing Strategy
A robust risk management strategy is paramount when engaging in fractional investing. Diversification across various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and alternative investments, can help to spread the risk and potentially reduce the impact of any single investment’s underperformance. Thorough due diligence and careful selection of investment platforms are also critical. Understanding the platform’s fees, regulations, and operational processes is essential.
Setting clear investment goals and risk tolerance levels, and adhering to them, are fundamental to a successful strategy.
Fractional investing lets you nibble on investments you might not be able to afford in full, like shares in a company or even Cryptocurrency. It’s a great way to diversify your portfolio, especially if you’re just starting out and want to dip your toes into various asset classes. It’s still a relatively new concept but is rapidly becoming more mainstream as a way to explore different investment opportunities without a large upfront cost.
Strategies to Mitigate Risk and Protect Capital
Implementing strategies to mitigate risk and safeguard capital is crucial in fractional investing. One such strategy involves creating a diversified portfolio, allocating investments across different asset classes and industries. Thoroughly researching companies and understanding their financial health, industry position, and management is essential. Understanding the fees and charges associated with fractional investing platforms is critical to making informed decisions.
Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments based on market conditions are also important. This ensures the portfolio remains aligned with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Table of Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Description | Mitigation Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illiquidity | Difficulty in quickly selling fractional shares | Diversify investments across multiple platforms and assets | Investing in a less-liquid, smaller-cap stock; selling takes longer. |
| Platform Risk | Problems with the fractional investing platform | Thoroughly research and select reputable platforms; understand their fees, regulations, and operational processes | Platform experiencing technical issues; halting trading. |
| Market Volatility | Fluctuations in market conditions | Diversify investments; have an emergency fund; set realistic expectations | Market downturn impacting overall returns. |
| Company-Specific Risk | Poor performance or financial issues of the underlying company | Thorough research; focus on established companies with strong financials; diversify across multiple companies | Company facing legal issues or industry challenges; impacting investment value. |
Fractional Investing and Diversification
Fractional investing offers a unique opportunity to diversify your portfolio, allowing you to invest in a wider range of assets than traditional methods often permit. This accessibility is particularly appealing for individuals with limited capital or those seeking a more balanced approach to portfolio management. By breaking down investment costs and simplifying access, fractional investing democratizes the benefits of diversification.Fractional investing empowers you to construct a diversified portfolio that mirrors the goals and risk tolerance of your investment strategy.
Diversification is a core tenet of sound investment practices. A diversified portfolio reduces the overall risk associated with any single investment. By spreading your capital across various asset classes, you lessen the impact of potential losses in one area on the entire portfolio.
Benefits of Diversification
A diversified portfolio is generally less volatile than one concentrated in a single asset class or a few stocks. This stability can provide a more consistent return over time. Diversification also allows you to potentially capture returns from different market sectors, reducing the impact of downturns in specific areas. A balanced approach across various asset classes can provide a more stable return profile, mitigating risk while aiming for potentially higher returns.
Asset Allocation in Fractional Investing
Asset allocation, the strategic distribution of your investment capital across different asset classes, is critical in fractional investing. A well-defined asset allocation strategy aligns your investment choices with your risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon. It’s important to consider factors such as market conditions, economic forecasts, and your personal circumstances when formulating your asset allocation plan.
Examples of Diverse Asset Allocations
Fractional investing provides the flexibility to create diverse portfolios tailored to specific needs and risk tolerances. For example, a portfolio designed for long-term growth might allocate a larger percentage to equities and a smaller portion to bonds. Conversely, a portfolio focused on income generation might allocate a larger percentage to fixed-income securities.
Fractional investing lets you invest in things like stocks or crypto, even if you only have a small amount of money. This is especially useful for getting into crypto, where platforms like Crypto exchanges offer fractional crypto purchases. It’s a great way to diversify your portfolio and potentially boost returns, even with small initial investments.
Comparison with Other Diversification Methods
Fractional investing offers a convenient and cost-effective way to diversify your portfolio compared to traditional methods like direct stock purchases. Direct investment in multiple stocks or funds can be time-consuming and require significant capital upfront. Fractional investing streamlines this process by allowing smaller investments in a variety of assets, thereby making diversification more accessible.
Examples of Diversified Fractional Investment Portfolios
| Asset Class | Allocation Percentage | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equities (US Stocks) | 40% | Exposure to the US stock market, potentially higher growth but higher risk. | Fractional shares in large-cap tech companies. |
| Bonds (Government Bonds) | 30% | Provides stability and income, generally lower risk than equities. | Fractional bonds issued by the US Treasury. |
| Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | 20% | Exposure to the real estate market, potentially higher returns. | Fractional shares in diversified REITs. |
| Alternative Investments (e.g., Gold) | 10% | Acts as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. | Fractional shares in gold-backed ETFs. |
Fractional Investing for Specific Investor Profiles
Fractional investing democratizes access to the stock market, making it more approachable for a wider range of investors. This accessibility, coupled with the potential for diversification, means various investor profiles can effectively utilize fractional investing. Understanding how different investor types can leverage this approach is crucial for maximizing its benefits.Different investors have unique goals, risk tolerances, and investment horizons.
Fractional investing adapts to these diverse needs by allowing investors to buy fractional shares of a wide array of securities, from established companies to emerging startups. This flexibility is a key advantage, enabling tailored investment strategies.
Beginner Investors
Beginner investors often lack the capital to invest in a substantial portfolio of individual stocks or bonds. Fractional investing provides a perfect solution. It allows them to begin investing with smaller amounts, gradually building their portfolios. This gradual approach reduces the risk of large losses and encourages disciplined investing. It also allows them to diversify their investments in a cost-effective manner.
By purchasing fractional shares of multiple companies, they can quickly build a diversified portfolio and gain experience in the market without a huge initial outlay.
Investment Strategies for Different Investor Types
Investors with different goals and risk tolerances can employ various strategies. Conservative investors, for instance, might focus on established blue-chip companies and dividend-paying stocks. Growth-oriented investors might favor emerging companies with high potential for growth, even if they carry more risk. Value investors may focus on companies they believe are undervalued.
Fractional investing lets you invest in things like stocks or even Bitcoin, Bitcoin , which can be a good way to diversify your portfolio. It’s a great option for those who want to get involved in the market without having to put down a large sum. You can still gain exposure to potentially lucrative assets like these with fractional investing.
Experienced Investors
Experienced investors often have larger portfolios and a deeper understanding of the market. Fractional investing can be valuable for these investors as well. It allows them to diversify their holdings even further, accessing a broader range of investments they might not otherwise have the capital for. This can be crucial in managing risk and achieving optimal portfolio diversification.
Fractional Investing Strategies for Various Investor Profiles
| Investor Profile | Investment Goals | Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Build a diversified portfolio with limited capital | Invest in fractional shares of several established companies across various sectors. Start with a small amount and gradually increase investments as confidence and capital grow. | Investing in fractional shares of technology giants (Apple, Microsoft, Google) and consumer staples (Coca-Cola, Procter & Gamble) |
| Conservative | Generate steady income and preserve capital | Prioritize dividend-paying stocks and bonds. Maintain a low-risk portfolio with established companies known for their consistent performance. | Investing in fractional shares of utilities (e.g., electric companies) and real estate investment trusts (REITs). |
| Growth-Oriented | Maximize potential returns, accepting higher risk | Invest in fractional shares of emerging companies with high growth potential. Explore sectors like technology, renewable energy, and biotechnology. | Investing in fractional shares of innovative tech startups or companies developing cutting-edge medical treatments. |
| Experienced | Diversify existing portfolio, manage risk, and potentially enhance returns | Invest in fractional shares of niche sectors or international companies to broaden diversification. Consider investing in small-cap or mid-cap companies. | Investing in fractional shares of international companies or sectors experiencing significant growth. |
Illustrative Examples of Fractional Investing
Fractional investing offers a flexible and accessible way to participate in the stock market, even with limited capital. This section provides concrete examples to illustrate how fractional investing works in practice, demonstrating its versatility and potential.These examples highlight different approaches to fractional investing, from building diversified portfolios to achieving specific financial goals. They showcase the strategies and benefits of this investment method, helping you visualize its practical application.
A Successful Fractional Investment Strategy Case Study
A young professional, Sarah, started with a modest $5,000 investment. Using a fractional investing platform, she allocated her funds across several promising tech stocks, including a few smaller companies. Over the next three years, her portfolio grew significantly, exceeding her initial expectations, due to a combination of solid company performance and smart portfolio diversification.
Different Fractional Investment Portfolios with Varied Objectives
Fractional investing enables diverse portfolio construction tailored to individual goals.
- Growth Portfolio: A portfolio focused on high-growth companies, possibly including emerging market stocks, often with a higher risk tolerance.
- Income Portfolio: Prioritizes dividend-paying stocks and real estate investment trusts (REITs) to generate regular income. The goal is passive income, rather than rapid growth.
- Conservative Portfolio: This approach leans toward established, stable companies, emphasizing capital preservation over high returns. It usually involves a lower level of risk.
Impact of Diversification Using Fractional Investing
Diversification is key to mitigating risk in any investment strategy. Fractional investing empowers individuals to diversify across various sectors and asset classes, even with a small capital base. This can be illustrated by a portfolio encompassing technology, healthcare, and consumer goods. Each sector responds differently to economic shifts, providing a buffer against potential downturns in one sector.
Growth Potential of Fractional Investing (Hypothetical Scenario)
Consider a hypothetical scenario where an investor allocates funds to a portfolio of five companies. Through fractional shares, they gain exposure to the growth potential of these companies. If the portfolio performs well, the investor will benefit from the collective growth of the constituent companies, possibly outpacing traditional savings accounts or fixed-income instruments.
Fractional Investing for Achieving Specific Financial Goals
Fractional investing can facilitate various financial objectives. For example, a young investor might allocate funds to a fractional investment portfolio designed to reach a specific savings goal, such as a down payment on a house or a child’s college fund.
Simulated Fractional Investment Portfolio
This simulated portfolio demonstrates the flexibility of fractional investing. It shows how small amounts can be used to access a variety of investments.
| Asset | Quantity | Cost Per Unit | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A Stock | 0.5 | $100 | $50 |
| Company B Bond | 1.2 | $50 | $60 |
| Company C ETF | 0.8 | $25 | $20 |
| Company D REIT | 0.3 | $150 | $45 |
Final Summary
In conclusion, fractional investing offers a powerful way to invest in a variety of assets with minimal upfront capital. It’s a valuable tool for beginners and seasoned investors alike, providing opportunities for diversification and potentially higher returns. The key is understanding the risks, selecting suitable platforms, and developing a strategy that aligns with your individual financial objectives.
FAQ Resource
What are the typical fees associated with fractional investing platforms?
Fees vary significantly between platforms. Some charge transaction fees, while others might have account maintenance or platform usage fees. Be sure to thoroughly review the platform’s fee structure before making any investments.
How do I choose a suitable fractional investing platform?
Consider factors like platform security, asset selection, user interface, and fees. Read reviews, compare features, and assess the platform’s reputation before committing to an account.
What is the minimum investment amount required for fractional investing?
Minimum investment amounts vary depending on the platform and asset. Some platforms have very low minimums, making fractional investing accessible to a wider range of investors.