Cross-border payments are essential for international trade and personal finance. From sending money to family abroad to facilitating global business transactions, understanding the nuances of these payments is crucial. This overview explores the various aspects of cross-border payments, from traditional methods to emerging technologies and the regulatory landscape.
Different payment methods, such as wire transfers and mobile wallets, have varying speeds and costs. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right method for your needs. Security is paramount, and fraud schemes can target cross-border transactions. This guide explores the risks and the security measures employed to protect your funds.
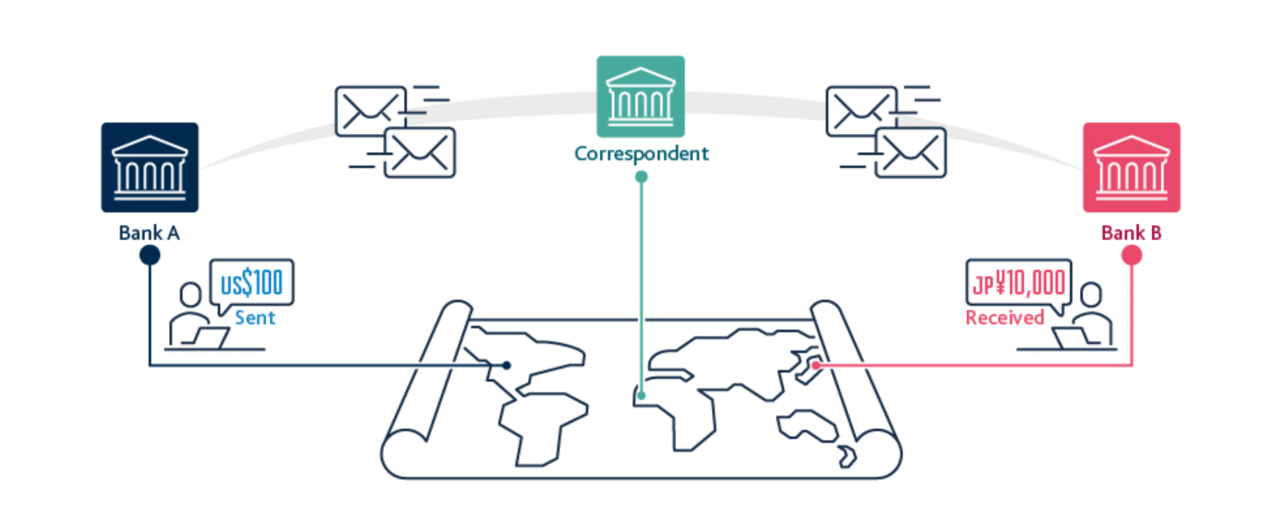
Introduction to Cross-border Payments
Source: surferseo.art
Cross-border payments facilitate financial transactions between parties located in different countries. They are essential for international trade, investment, and remittances, enabling individuals and businesses to send and receive money across geographical boundaries. Understanding the intricacies of these transactions is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global financial landscape.Cross-border payments encompass a wide range of methods, each with its own characteristics and implications.
From traditional wire transfers to innovative mobile payment systems, the options available to send and receive funds internationally are continuously evolving. This evolution is driven by the need for faster, more efficient, and secure methods to facilitate global financial flows.
Cross-border payments can be tricky, involving lots of steps and potential fees. But the rise of contactless payments is making things much smoother. Using Contactless payments systems could significantly reduce the hassle and cost of international transactions. This could lead to a more efficient and less expensive way to handle cross-border payments for businesses and individuals alike.
Different Types of Cross-border Payment Methods
Various methods are available for cross-border payments, each with unique characteristics. These methods vary significantly in terms of speed, cost, security, and accessibility.
Cross-border payments can be a real headache, with lots of fees and complicated processes. Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) solutions are changing that, making it easier for businesses to handle international transactions. This streamlined approach is promising for simplifying cross-border payments in the future.
- Wire Transfers: A traditional method, wire transfers involve transferring funds through a bank’s network. They are generally suitable for large sums of money and often used for business transactions or international money transfers. They tend to be slower than other methods, with processing times typically ranging from one to several business days.
- Mobile Payments: Mobile payment platforms, such as international mobile wallets, facilitate payments using smartphones. These platforms are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenience and speed, particularly for smaller transactions. Processing times for mobile payments can be significantly faster, often within hours, depending on the platform and the specific transaction.
- ACH (Automated Clearing House) Payments: These domestic US-based transfers, are commonly used for person-to-person (P2P) or business-to-business (B2B) payments within the United States. They typically involve electronic transfers between banks and are often used for payroll or bill payments. While not directly cross-border, they illustrate the underlying electronic infrastructure used in many international transfers.
- Real-time Payments: This method enables near-instantaneous fund transfers, commonly used for domestic payments within a country. While real-time payments are increasingly used in international transactions, the infrastructure and regulatory frameworks vary by country, which can influence the processing time.
Key Actors in Cross-border Payments
Several entities play crucial roles in facilitating cross-border transactions.
- Banks: Banks act as intermediaries in the process, handling funds transfer between accounts in different countries. They often charge fees for these services.
- Payment Processors: These companies specialize in processing payments, often offering services for merchants and businesses facilitating international transactions. They streamline the process and often provide more competitive pricing than banks.
- Money Transfer Operators: These companies, sometimes called remittance companies, specialize in facilitating international money transfers between individuals or businesses. They are often focused on providing affordable solutions, particularly for smaller transactions.
Cross-border Payment Methods Comparison
| Payment Method | Typical Use Cases | Average Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Transfer | Large international payments, business transactions | 1-5 business days |
| Mobile Payments | Person-to-person (P2P) transfers, small-value transactions | Few hours |
| ACH Payments | Domestic payments in the US | Usually same-day |
| Real-time Payments | Domestic payments within a country, increasingly used in cross-border | Near-instantaneous |
Challenges and Risks in Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments, while essential for global commerce, are fraught with complexities. Businesses and individuals alike face a range of obstacles, from fluctuating exchange rates and lengthy processing times to security concerns and potential fraud. Understanding these challenges is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring smooth international transactions.
Common Challenges Faced by Businesses and Individuals
International transactions often involve numerous intermediaries, each with its own fees and processing times. This can lead to substantial costs and delays. Currency exchange rates fluctuate, impacting the final amount received or paid, and these variations can be difficult to predict. Moreover, differing regulations and compliance requirements across countries add complexity to the process. The various legal and regulatory frameworks can be challenging to navigate, especially for smaller businesses or individuals unfamiliar with international commerce.
Security Risks Associated with International Payments, Cross-border payments
Security is paramount in cross-border payments. Cybercriminals often target international transactions due to the potential for high financial gain. Phishing scams, malware attacks, and identity theft are significant threats. Data breaches can compromise sensitive financial information, leading to significant financial losses. The lack of a centralized regulatory body to oversee international transactions can create a regulatory gap that criminals exploit.
Furthermore, the use of multiple payment processors and platforms, each with its own security protocols, can create vulnerabilities if not carefully managed.
Fraud Schemes Targeting Cross-border Payments
Numerous fraudulent schemes target cross-border payments. One common tactic is phishing, where criminals impersonate legitimate institutions to obtain sensitive information. Money laundering, where illicit funds are disguised as legitimate transactions, is another serious concern. Fake invoices, often associated with fraudulent contracts, are another frequently employed tactic. Additionally, scams involving fake goods or services can lead to financial losses for victims.
Comparison of Security Measures Employed by Different Payment Processors
Different payment processors employ various security measures to protect transactions. A comparison of these measures can highlight the varying levels of security provided. The table below illustrates the common security protocols employed by different processors. Factors such as encryption methods, authentication procedures, and transaction monitoring are key considerations in evaluating the security posture of each processor.
| Payment Processor | Encryption Methods | Authentication Procedures | Transaction Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visa | Advanced encryption standards (AES) | Multi-factor authentication (MFA) | Real-time fraud detection systems |
| MasterCard | Secure Socket Layer (SSL) | Strong passwords and biometric verification | Suspicious activity monitoring |
| PayPal | Industry-standard encryption | User account verification | Transaction history analysis |
| Western Union | Secure communication channels | Customer identification | Transaction monitoring and reporting |
Technological Advancements in Cross-border Payments
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing the cross-border payment landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, security, and cost reduction. These advancements are streamlining international transactions, making them faster, cheaper, and more transparent for businesses and individuals alike.Technological advancements are significantly impacting the efficiency and cost of cross-border payments. The traditional methods, often reliant on intermediaries and complex processes, are being challenged by innovative solutions.
These new approaches are redefining how international transactions are handled, offering more streamlined pathways for global commerce.
Impact of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and secure nature, is transforming cross-border payment systems. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and processing times. By recording transactions on a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain enhances transparency and security, mitigating fraud risks. This distributed ledger technology allows for direct peer-to-peer transactions, removing reliance on traditional financial institutions. A notable example is the use of blockchain for international remittances, enabling faster and cheaper transfers between individuals and businesses across borders.
Cryptocurrencies in Cross-border Payments
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and others, are gaining traction in the cross-border payment space. Their potential to bypass traditional banking systems and reduce transaction fees makes them appealing for international transfers. The ability to make payments directly between parties, without relying on intermediaries, can offer considerable cost savings. However, regulatory uncertainties and volatility remain significant challenges. The use of stablecoins, cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies, is emerging as a solution to mitigate the volatility concerns, offering a more stable alternative for cross-border transactions.
Cross-border payments are becoming increasingly important, especially for global businesses. Modern digital solutions, like those offered through Digital finance , are streamlining these transactions and making them faster and more efficient. This ultimately helps businesses operate more smoothly on an international scale.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Emerging Technologies
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Reduced transaction costs, increased transparency, enhanced security, faster processing times | Scalability issues, regulatory uncertainties, potential for misuse |
| Cryptocurrencies | Reduced transaction fees, potential for faster transfers, direct peer-to-peer transactions | Volatility of cryptocurrency values, regulatory hurdles, security concerns |
| Mobile Payments | Convenience, accessibility, lower transaction costs for consumers | Security risks, dependence on mobile infrastructure, limited acceptance in some regions |
| Real-time Payments | Faster transaction processing, improved efficiency for businesses | Potential for errors, technical glitches in the system |
Regulatory Landscape of Cross-border Payments
Navigating the intricate world of cross-border payments requires a deep understanding of the diverse regulatory landscapes across different regions. These frameworks, often complex and overlapping, significantly impact the efficiency and security of international transactions. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, ensuring smooth operations and avoiding potential penalties.The regulatory environment for cross-border payments is in a constant state of evolution, adapting to new technologies and emerging risks.
International organizations play a key role in harmonizing standards and fostering cooperation among nations to address the challenges of cross-border transactions.
Different Regulatory Frameworks
Various countries and regions employ distinct regulatory frameworks for cross-border payments. These frameworks often differ in their approach to oversight, compliance requirements, and penalties for non-compliance. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses operating globally. For instance, the European Union has a unified regulatory framework, the Payment Services Directive (PSD2), that applies to all member states, while the regulations in the Asia-Pacific region are more diverse and often vary significantly by country.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the SWIFT, play a crucial role in establishing standards and best practices for cross-border payments. These organizations work to improve transparency, security, and efficiency in the global payment system. The BIS, for example, promotes international cooperation and research on financial stability, influencing regulatory frameworks globally.
Evolving Regulatory Environment for Digital Currencies
The rapid rise of digital currencies like Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is reshaping the regulatory environment for cross-border payments. Governments are actively working to define the regulatory framework for these digital assets, addressing issues such as money laundering, tax compliance, and consumer protection. The approach to regulating cryptocurrencies varies considerably. Some jurisdictions are embracing digital currencies, establishing clear regulatory frameworks, while others are adopting a more cautious approach.
Regulatory Approaches of Different Bodies
Different regulatory bodies employ various approaches to overseeing cross-border payments. Central banks, financial regulatory authorities, and other agencies often have distinct mandates and priorities. For example, central banks often focus on the stability of the financial system, while financial regulatory bodies may concentrate on consumer protection and market integrity. These varying approaches often lead to differing compliance requirements and oversight measures.
The interplay between these different authorities requires careful consideration for businesses operating internationally. Understanding the specific regulatory landscape in each target market is critical for successful cross-border payments. The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, for example, has a clear framework for regulating payment institutions and safeguarding consumers, while the Federal Reserve in the US focuses on the overall stability of the financial system.
Global Payment Systems and Infrastructure
Cross-border payments rely heavily on global payment systems and robust infrastructure. These systems facilitate the transfer of funds across international borders, enabling businesses and individuals to conduct transactions efficiently. Understanding the different networks, their strengths and weaknesses, and the underlying infrastructure is crucial for navigating the complexities of cross-border commerce.The various global payment systems operate on different principles and use varying technologies, influencing the speed, cost, and security of transactions.
Their infrastructure encompasses everything from secure communication channels to robust settlement mechanisms, ensuring the smooth flow of funds.
Key Global Payment Systems
Different payment systems cater to various needs and preferences. Some systems are geared towards high-value transactions, while others specialize in lower-value, consumer-focused transfers. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate system for a given transaction.
- SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication): A prominent system for international money transfers between banks. It uses a standardized messaging format, enabling banks to communicate securely and efficiently. SWIFT’s global reach and established reputation contribute to its reliability, though it can be expensive for smaller transactions.
- Visa and Mastercard: These are ubiquitous credit and debit card networks that process a vast volume of cross-border transactions. Their extensive global acceptance and established infrastructure make them popular for consumer payments. However, they typically charge transaction fees and may have higher processing times compared to direct bank transfers.
- International Bank Transfers: Direct bank transfers are often used for high-value transactions between businesses or individuals with existing banking relationships. This method offers greater control over the process, but it can be slower and less transparent than other systems.
- Real-time Gross Settlement Systems (RTGS): These systems allow for the immediate settlement of payments between banks, significantly reducing transaction time. While RTGS systems offer speed, they may not be universally available or affordable for all types of transactions.
Features and Functionalities Comparison
A comparative analysis of the features and functionalities of these payment systems reveals key distinctions. This comparison aids in selecting the most suitable option based on specific transaction needs.
Cross-border payments can be a real headache, with high fees and slow processing times. Luckily, Fintech startups are stepping in to revolutionize the way we send and receive money internationally. These innovative companies are creating new, faster, and cheaper solutions for cross-border transactions, making global commerce much more efficient.
| Payment System | Speed | Cost | Security | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWIFT | Variable (often slower than RTGS) | Higher for smaller transactions | High, through encryption and security protocols | Extensive global coverage, mainly for banks |
| Visa/Mastercard | Variable, often slower than direct transfers | Transaction fees, variable based on transaction size | Generally secure, with fraud prevention measures | Widely accepted by merchants and consumers |
| International Bank Transfers | Slower | Lower fees compared to SWIFT but can vary | High security protocols used by banks | Dependent on banking relationships |
| RTGS | Very fast (real-time) | Variable, often higher than other systems | High, with robust security measures | Limited availability, often for high-value transactions |
Infrastructure Requirements
Seamless cross-border payments demand a sophisticated infrastructure. This encompasses secure communication channels, robust payment processing systems, and reliable settlement mechanisms.
- Secure Communication Channels: Encryption and data security protocols are essential to protect sensitive financial information during transmission.
- Real-time Payment Systems: Modern systems must facilitate the immediate transfer of funds between parties.
- Interbank Agreements and Protocols: Standardized agreements and protocols between banks and payment networks are crucial for seamless transactions.
- Settlement Mechanisms: Efficient mechanisms for settling transactions across different jurisdictions are critical.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Global Payment Networks
A summary table highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of various global payment networks is presented below.
| Payment Network | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| SWIFT | Wide global reach, standardized protocols, high security | Can be expensive for small transactions, slower than some alternatives |
| Visa/Mastercard | Wide acceptance, established infrastructure, consumer-friendly | Transaction fees, slower than direct transfers, potentially higher fraud risk |
| International Bank Transfers | Greater control over the process, lower fees in some cases | Slower processing, limited transparency, less readily accessible |
| RTGS | Fast real-time settlement, high security | High costs, limited availability, suitable only for high-value transactions |
Cost and Efficiency Considerations in Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments, while vital for global commerce, often come with significant cost and efficiency challenges. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies to mitigate them is crucial for businesses operating internationally. Minimizing costs and optimizing transaction times directly impact profitability and competitiveness in the global market.International transactions are inherently complex. Exchange rate fluctuations, numerous intermediaries, and varying regulations across countries all contribute to the overall cost.
Efficient management of these costs is essential for businesses to thrive in a globalized economy.
Factors Influencing Cross-border Payment Costs
Exchange rate fluctuations are a major driver of cross-border payment costs. Changes in currency values can significantly impact the amount of foreign currency received or paid, leading to unexpected expenses. Transaction fees charged by payment processors and banks vary considerably depending on the payment method, transaction amount, and the involved parties’ locations. Transfer time, including processing time and settlement time, is another crucial element.
Slower processing times can lead to missed deadlines and lost opportunities.
Strategies for Reducing Cross-border Payment Costs
Several strategies can help businesses reduce costs associated with international transactions. Negotiating favorable exchange rates with banks or financial institutions is a key strategy. Using specialized cross-border payment solutions designed for international transactions can often offer lower fees than traditional methods. Businesses should also explore the use of technology to streamline their payment processes. Employing automated payment systems and digital platforms can significantly reduce manual processing time and associated costs.
Cross-border payments can be a real headache, with lots of fees and complicated processes. But the rise of QR code payments is making things a lot simpler. QR code payments are quickly becoming a popular way to send and receive money internationally, promising faster and cheaper transactions. This could revolutionize how businesses and individuals handle cross-border payments.
Optimizing Cross-border Payment Processes
Many businesses optimize their cross-border payment processes through careful selection of payment providers. For example, some companies use payment providers with specialized expertise in international transactions to benefit from lower fees and faster processing times. They also implement internal controls to monitor transactions and identify potential cost savings. Tracking payment costs is crucial. Businesses often use software or dedicated tools to monitor and analyze payment costs across different transactions and regions.
These systems enable them to identify patterns and trends in costs, allowing for targeted cost reduction strategies.
Methods for Tracking and Managing Cross-border Payment Costs
Regularly monitoring and analyzing cross-border payment costs is vital. Businesses can use detailed transaction reports generated by their payment providers. These reports provide insights into transaction fees, exchange rates, and processing times. By comparing these reports over time, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities. For example, a business might discover that a specific payment provider consistently charges higher fees than others.
Implementing a centralized payment platform can improve tracking and control of payments. Using this platform, companies can track payments in real-time and gain insights into trends. Spreadsheet software or dedicated accounting software can help with the aggregation and analysis of payment data. Analyzing trends in payment costs can provide valuable information for future financial planning.
Case Studies of Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments, while vital for global commerce, often present unique challenges. Understanding how different companies and organizations navigate these complexities, and the impact of innovation, is crucial for successful international transactions. Successful implementations serve as blueprints, highlighting best practices and providing valuable insights into the intricacies of cross-border finance.
Successful Cross-border Payment Implementations
Various companies have successfully implemented cross-border payment systems, demonstrating resilience and adaptability in the face of evolving regulatory landscapes and technological advancements. These implementations highlight best practices and solutions that can be adapted by other organizations. For example, a multinational corporation might use a specialized payment platform that streamlines transactions across numerous countries, ensuring timely and secure funds transfer.
- E-commerce giants frequently leverage sophisticated payment gateways for international transactions, enabling seamless purchasing experiences for customers worldwide. These platforms often employ multiple payment processors to accommodate various currencies and regional regulations.
- Financial institutions frequently employ cutting-edge technologies, such as blockchain and API integrations, to improve efficiency and security in international money transfers. These technologies facilitate real-time tracking and automated reconciliation of transactions.
- Logistics companies have implemented integrated payment systems for handling international freight and import/export transactions. These systems often include automated invoicing and payment processing, enabling efficient tracking of goods and finances across borders.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have significantly impacted cross-border payments, streamlining processes and reducing costs. Examples include the rise of digital wallets, peer-to-peer (P2P) payment systems, and mobile banking, all of which have made international transactions more accessible and convenient.
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize cross-border payments by enabling faster, more secure, and transparent transactions. Cryptocurrency platforms are examples of how blockchain facilitates direct peer-to-peer transfers, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries.
- Mobile payment solutions are gaining popularity, particularly in emerging markets. These solutions provide a user-friendly interface for conducting international transfers, often integrating with local payment systems for seamless transactions.
- Real-time payment systems are becoming increasingly prevalent, enabling almost instantaneous fund transfers across borders. This has significant implications for businesses involved in international trade, particularly those needing immediate access to funds for timely payments.
Challenges and Solutions in Specific Scenarios
Cross-border payment scenarios frequently present unique challenges. Solutions adopted by various organizations often involve careful consideration of regional regulations, currency fluctuations, and security protocols.
| Scenario | Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| International Trade | High transaction costs, varying exchange rates | Utilizing specialized payment platforms, optimizing transaction routes, and leveraging hedging strategies. |
| Remittances | High fees, delays, lack of transparency | Using low-cost payment providers, ensuring secure transfers, and incorporating real-time tracking. |
| Cross-border investments | Regulatory complexities, currency risks | Consulting with legal experts, managing currency fluctuations through hedging, and complying with local regulations. |
Process of International Payments for Various Industries
The process of conducting international payments varies depending on the industry and the specific requirements of the transaction. However, common elements include transaction initiation, payment processing, and settlement.
- E-commerce typically involves a secure online payment gateway, often integrated with a payment processor. This gateway facilitates the transaction and ensures the funds are transferred to the recipient’s account.
- Financial institutions use specialized software and secure channels for processing international transactions. These systems often incorporate real-time tracking and reconciliation to ensure accuracy and timely settlements.
- Logistics companies use a complex network of intermediaries and payment platforms to track and manage payments for international shipments. This process often involves multiple currencies and diverse payment methods.
Future Trends in Cross-border Payments
The cross-border payments landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting regulatory environments. This evolution promises increased efficiency, lower costs, and greater accessibility for international transactions. Understanding these future trends is crucial for businesses and individuals alike to navigate the changing global financial ecosystem.
Predicted Direction of Cross-border Payment Systems
Cross-border payment systems are expected to become more streamlined and automated. This automation will be achieved through the integration of various technologies, leading to faster processing times and reduced errors. Real-time settlement capabilities are likely to become standard, further accelerating transactions and improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, systems will likely prioritize security, implementing robust authentication and fraud prevention measures to safeguard sensitive financial data.
Influence of Technological Developments
Technological advancements are reshaping international transactions in profound ways. Blockchain technology, with its potential for secure and transparent record-keeping, is poised to revolutionize cross-border payments. Cryptocurrencies, while still facing regulatory hurdles, could become more integrated into mainstream payment systems, offering alternative methods for international transfers. Mobile payments and digital wallets will continue to gain traction, enabling easier and more convenient transactions for individuals and businesses across borders.
Furthermore, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for fraud detection and risk assessment will likely become more sophisticated, leading to more secure and reliable transactions.
Potential Disruptions and Innovations
The cross-border payments industry is likely to see several disruptions and innovations. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms may emerge as viable alternatives to traditional financial institutions, offering potentially lower transaction costs and greater accessibility. The use of smart contracts for automating payment processes will become more common, leading to greater efficiency and reduced reliance on intermediaries. New payment methods utilizing emerging technologies, such as biometrics and neural networks, will likely be introduced.
Evolution of Global Payment Infrastructure
Global payment infrastructure will likely undergo significant transformation. A greater focus on interoperability between different payment systems will become critical to reduce friction and enhance efficiency. The use of open banking standards will facilitate seamless data exchange between financial institutions, potentially enabling new payment models and services. Infrastructure improvements in developing countries will be essential to bridge the gap in access to financial services globally.
This includes investments in digital infrastructure and financial literacy programs. The establishment of standardized global payment protocols will likely become a necessity, promoting interoperability and efficiency.
Specific Examples of Future Trends
The increasing use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for seamless integration between different payment systems is a prime example. For instance, businesses will be able to integrate various payment gateways and platforms directly into their software, significantly streamlining the payment process for customers. Another example is the use of AI in predicting potential fraud risks. Sophisticated algorithms will analyze transaction data in real-time, enabling faster and more accurate fraud detection.
This predictive capability can significantly reduce the risk of fraudulent activities.
Summary
In conclusion, navigating the world of cross-border payments requires a deep understanding of various factors, including payment methods, security risks, technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and global payment systems. This discussion highlighted the complexities and opportunities in international financial transactions. Staying informed about these factors will help businesses and individuals make informed decisions and optimize their cross-border payment processes.
Popular Questions
What are the most common fraud schemes targeting cross-border payments?
Phishing, scams involving fake payment portals, and identity theft are common. Be cautious of unsolicited emails or messages requesting payment details.
What are the typical costs associated with cross-border payments?
Exchange rate fluctuations, transaction fees, and transfer time are key cost considerations. Different payment methods have different fee structures.
How can I reduce the costs of cross-border payments?
Look for payment providers with competitive exchange rates and low fees. Consider using a payment method that aligns with your needs, considering speed and security.
What are some emerging technologies impacting cross-border payments?
Blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and faster payment systems are changing how international transactions are processed. These technologies often offer improved efficiency and reduced costs.